- Metadoro
- Products
- Metadoro academy
- Diversification and asset allocation
Diversification and asset allocation
In this section, we will discuss concepts such as:
- Diversification once again and why it's important
- Correlation
- Portfolio risk
- Expected return
Let's look at the top S&P500 gainer and looser stocks of 2020:
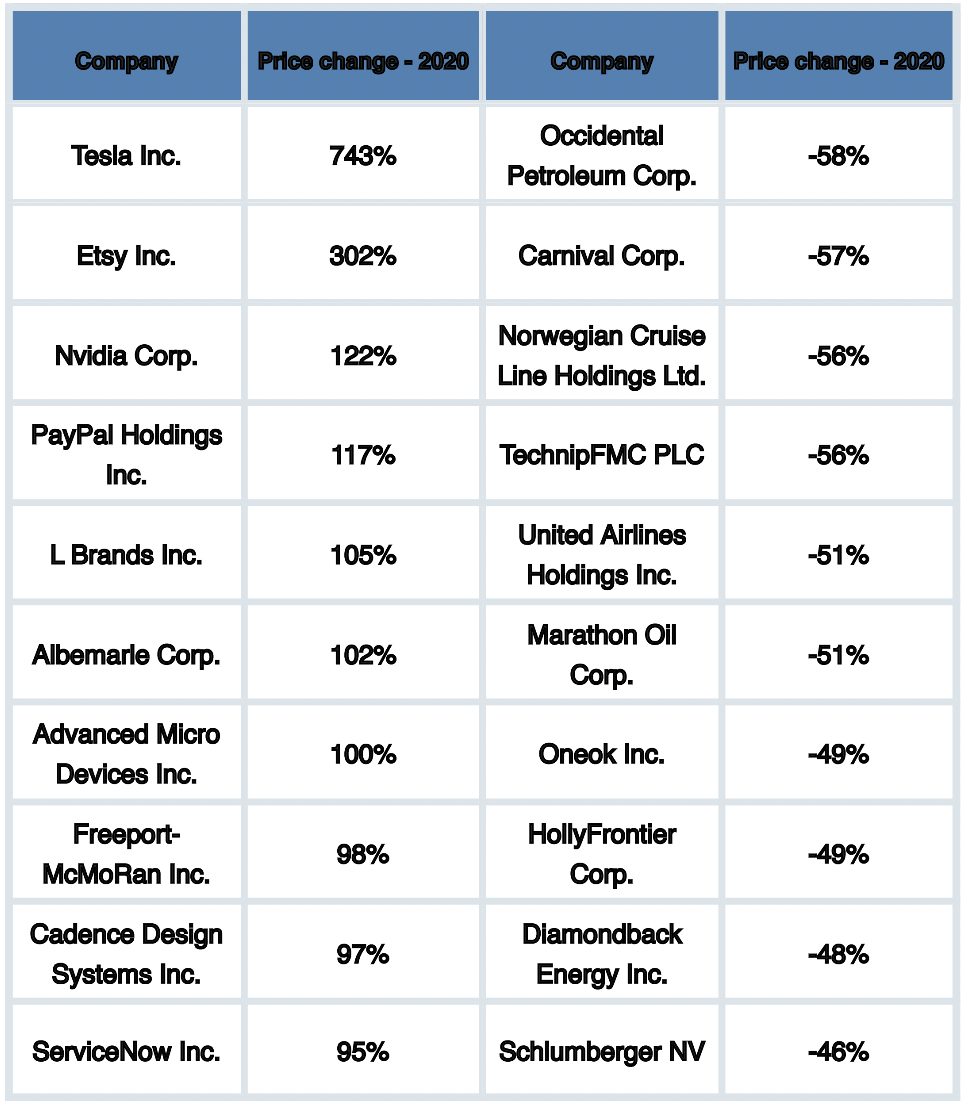
So, let's imagine that despite the overall growth of the S&P500 index, we invested in a company from the list of underperformers. Looking at the annual performance of the stock, any of us would ask - why bother with all of this? Who could have predicted the pandemic and such a blow to the tourism industry? And what if I had bought shares in, let's say, Carnival Corp.
To minimize the impact of such events on the outcome of our investments exists…
Diversification
Diversification is a strategy used in investing to reduce risk by spreading investments across various assets or asset classes. Doing so aims to balance potentially higher returns and lower risk.
The idea behind diversification is to avoid putting all your resources into a single investment or asset, which can be highly vulnerable to specific market events or economic changes. Instead, it involves allocating your investments across different types of assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, or within the same asset class but in various sectors or industries. This approach mitigates the impact of poor performance in one area by potentially benefiting from better performance in others.
Diversification aims to reduce the overall volatility of a portfolio and improve its chances of achieving more stable and consistent returns over time.
"Don't put all your eggs in one basket" - the golden rule of diversification.
Standard Deviation
Standard deviation is the primary tool for measuring risk. It helps investors assess how much their investments may fluctuate in value over time.
In simpler words:
High Standard Deviation in Investing: Imagine a roller coaster. If a stock's price goes up and down a lot, from $100 to $30 to $150 in a year, it has a high standard deviation. It's like a wild ride with big jumps.
Low Standard Deviation in Investing: Now, think of a calm lake. If a stock's price stays steady around $100 throughout the year, it has a low standard deviation. It's like a smooth, predictable ride with tiny up-and-down movement.
In investing, high standard deviation means more risk and uncertainty, while low standard deviation means less risk and more stability. Investors choose investments based on how much "roller coaster" they're comfortable with in their portfolios.
Let's illustrate how diversification can reduce standard deviation with an example:
Imagine you have two stocks in your portfolio: Stock A and Stock B.
Stock A:
- Standard Deviation: 20%
- Expected Return: 10%
Stock B:
- Standard Deviation: 30%
- Expected Return: 12%
Now, let's see what happens when you combine these two stocks in different ways:
Portfolio 1: You invest 50% of your money in Stock A and 50% in Stock B.
- Portfolio Standard Deviation = 0.5 * 20% + 0.5 * 30% = 25%
- Portfolio Expected Return = 0.5 * 10% + 0.5 * 12% = 11%
Portfolio 2: You invest 75% of your money in Stock A and 25% in Stock B.
- Portfolio Standard Deviation = 0.75 * 20% + 0.25 * 30% = 22.5%
- Portfolio Expected Return = 0.75 * 10% + 0.25 * 12% = 9.5%
Portfolio 3: You invest 25% of your money in Stock A and 75% in Stock B.
- Portfolio Standard Deviation = 0.25 * 20% + 0.75 * 30% = 27.5%
- Portfolio Expected Return = 0.25 * 10% + 0.75 * 12% = 11.5%
As you can see, by combining these two stocks in different proportions, you can create portfolios with varying levels of risk (measured by standard deviation) and expected returns. Diversifying your investments by spreading your money across different assets or stocks allows you to adjust the risk-return profile of your portfolio to align with your investment goals and risk tolerance. In this example, Portfolio 2 achieved a lower standard deviation than either Stock A or Stock B individually, showcasing how diversification can help reduce overall risk.
But can we completely eliminate that risk?
Correlation: The Inescapable Factor
We've learned that the risk goes down when we spread our investments (diversify). But we can't make risk disappear completely.
The reason is something called "correlation." It's like the glue that ties investments together.
Imagine you hear, "The stock market is falling." This doesn't mean every single stock is falling, but a bunch of them are. It's like a flock of birds flying together.
Correlation comes in two flavors: positive (when investments move together) and negative (when they move in opposite directions).
Generally, if two investments are in similar businesses, they follow each other's lead.









